Waterproof cold-pressed terminals are specialized electrical connectors that provide moisture-resistant connections through mechanical compression without heat application. These terminals combine sealed enclosures with cold-forming crimp technology to create reliable electrical connections in harsh environments where water ingress could cause system failure.
Understanding the design principles and selection criteria for waterproof cold-pressed terminals is critical for ensuring electrical system reliability in marine, automotive, industrial, and outdoor applications where moisture protection directly impacts safety and performance.
What Are Waterproof Cold-Pressed Terminals?
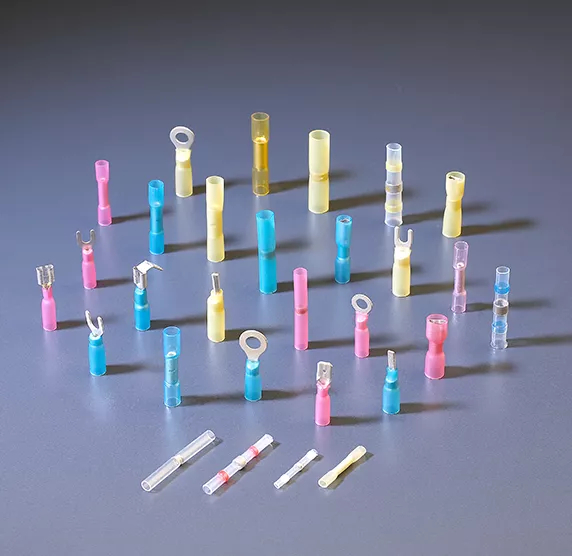

Waterproof cold-pressed terminals are electrical connection devices that create secure, moisture-resistant joints between wires and electrical components through mechanical compression at ambient temperature. Unlike heat-applied connections, cold-pressing uses controlled force to form gas-tight seals while maintaining the electrical and mechanical integrity of the connection.
Key Components:
- Terminal body: Metal conductor (typically copper or brass)
- Sealing elements: O-rings, gaskets, or molded seals
- Compression mechanism: Designed for cold-forming crimp tools
- Protective housing: Waterproof enclosure rated to specific IP standards
Design Principles for Waterproof Cold-Pressed Terminals
1. Moisture Barrier Engineering
Primary Sealing Methods:
- O-ring seals: Elastomeric rings providing 360-degree protection
- Overmolded seals: Injection-molded barriers integrated into terminal design
- Compressed gaskets: Flat sealing elements activated by compression force
- Thread sealing: Tapered or parallel threads with sealant compounds
2. Material Selection Criteria
| Material Property | Standard Requirement | Performance Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Conductor Material | Copper alloy (99.9% min) | Electrical conductivity |
| Seal Material | NBR, EPDM, or Silicone | Temperature/chemical resistance |
| Housing Material | Nylon, PVC, or Polyethylene | UV and impact resistance |
| Plating | Tin, Silver, or Gold | Corrosion protection |
3. Compression Force Engineering
Critical Design Parameters:
- Crimp force specification: 500-3000 lbs depending on gauge
- Compression ratio: 70-80% of original wire diameter
- Deformation control: Prevents over-compression damage
- Cold-flow characteristics: Maintains seal integrity over time
4. IP Rating Compliance Standards
Ingress Protection Classifications:
- IP67: Dust-tight and waterproof to 1 meter depth
- IP68: Dust-tight and waterproof beyond 1 meter
- IP69K: High-pressure, high-temperature wash protection
Expert Tip: Always verify IP rating test conditions match your application requirements. IP68 depth and duration specifications vary by manufacturer.
Comprehensive Comparison: Terminal Types and Applications
| Terminal Type | IP Rating | Max Voltage | Temperature Range | Primary Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ring Terminals | IP67-IP68 | 600V | -40°C to +105°C | Marine electrical panels |
| Spade Terminals | IP67 | 300V | -40°C to +85°C | Automotive connections |
| Bullet Connectors | IP68 | 50V | -20°C to +80°C | Motorcycle/ATV wiring |
| Pin Terminals | IP67 | 1000V | -55°C to +125°C | Industrial control systems |
| Splice Connectors | IP68 | 600V | -40°C to +90°C | Underwater cable joints |
Applications and Use Cases

Marine Electronics
Waterproof cold-pressed terminals are essential for:
- Navigation equipment connections: GPS, radar, and communication systems
- Bilge pump circuits: Critical safety system reliability
- Deck lighting: Exposure to spray and submersion
- Engine compartment wiring: Oil and water contamination protection
Automotive Systems
Critical applications include:
- Engine bay connections: Heat and moisture resistance
- Trailer wiring: Road salt and weather exposure
- Underhood sensors: Temperature and pressure monitoring
- Lighting circuits: Headlamps and signal systems
Industrial Environments
Primary uses encompass:
- Process control wiring: Chemical and wash-down areas
- Outdoor equipment: Weather station and monitoring devices
- Food processing: Sanitary wash-down compliance
- Mining equipment: Dust and moisture protection
Step-by-Step Selection Process
Step 1: Environmental Assessment
- Identify moisture exposure level: Splash, immersion, or high-pressure wash
- Determine temperature extremes: Operating and storage ranges
- Assess chemical exposure: Oils, salts, acids, or cleaning agents
- Evaluate mechanical stress: Vibration, flexing, and pull forces
Step 2: Electrical Requirements Analysis
- Calculate current carrying capacity: Continuous and surge ratings
- Determine voltage requirements: Operating and breakdown voltages
- Assess insulation needs: Working voltage and safety margins
- Consider signal integrity: Low-noise and impedance requirements
Step 3: Mechanical Specification
- Wire gauge compatibility: Ensure proper crimp range
- Connection type: Ring, spade, pin, or splice configuration
- Mounting requirements: Panel thickness and access constraints
- Maintenance accessibility: Service and inspection needs
Step 4: Compliance Verification
- Industry standards: UL, CSA, IEC, or marine certifications
- Environmental ratings: IP67, IP68, or IP69K requirements
- Safety approvals: Hazardous location classifications if applicable
- Quality certifications: ISO 9001 or automotive standards
Safety Warning: Never exceed manufacturer-specified crimp force ranges. Over-compression can damage seals and create failure points.
Expert Selection Criteria
Quality Indicators
- Crimp inspection windows: Visual verification of proper compression
- Color-coded sizing: Prevents incorrect wire gauge selection
- Pre-insulated designs: Factory-applied insulation and sealing
- Strain relief integration: Cable protection at terminal entry
Performance Validation Methods
- Salt spray testing: ASTM B117 corrosion resistance verification
- Thermal cycling: Temperature expansion/contraction durability
- Immersion testing: Long-term waterproof integrity
- Pull-out testing: Mechanical retention strength verification
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Moisture Ingress Problems
Symptoms: Corrosion, voltage drop, or intermittent connections
Solutions:
- Verify proper crimp force application
- Check O-ring or gasket condition
- Ensure thread engagement and sealant application
- Validate IP rating for application severity
Mechanical Failure
Symptoms: Loose connections or terminal separation
Solutions:
- Confirm wire gauge and terminal compatibility
- Verify crimp tool calibration and condition
- Check for over-compression damage
- Assess vibration and thermal stress factors
Electrical Performance Issues
Symptoms: Voltage drop, heating, or signal degradation
Solutions:
- Verify conductor material and plating integrity
- Check contact surface cleanliness and condition
- Confirm proper torque specifications for threaded connections
- Assess current carrying capacity versus load requirements
Professional Installation Guidelines
Required Tools and Equipment
- Calibrated crimp tools: Proper dies for terminal type and wire gauge
- Torque wrenches: For threaded connection specifications
- Inspection equipment: Magnification and crimp force verification
- Testing instruments: Multimeters and insulation resistance testers
Installation Best Practices
- Wire preparation: Strip length and surface cleanliness verification
- Terminal inspection: Visual examination for damage or contamination
- Crimp execution: Single compression cycle with proper positioning
- Seal verification: O-ring placement and sealant application
- Connection testing: Electrical continuity and insulation resistance
Quality Control Checkpoints
- Visual inspection: Proper compression and seal integrity
- Pull testing: Mechanical retention verification (10% sample minimum)
- Electrical testing: Resistance and insulation measurements
- Documentation: Installation records and test results
Frequently Asked Questions
What’s the difference between IP67 and IP68 waterproof ratings?
IP67 terminals are waterproof when immersed up to 1 meter depth for 30 minutes, while IP68 provides protection beyond 1 meter depth. The specific depth and duration for IP68 must be defined by the manufacturer, as it varies based on design and application requirements.
How do you determine the correct crimp force for waterproof terminals?
Crimp force depends on wire gauge, terminal design, and material properties. Always follow manufacturer specifications, typically ranging from 500-3000 lbs. Use calibrated tools and verify crimp quality through pull testing and visual inspection of the compression profile.
Can waterproof cold-pressed terminals be reused after removal?
No, waterproof terminals should never be reused. The cold-pressing process permanently deforms both the terminal and wire, and removing the connection compromises the seal integrity and mechanical strength. Always install new terminals for replacement connections.
What temperature ranges can waterproof terminals handle?
Temperature ranges vary by material composition, typically from -40°C to +125°C for high-performance terminals. Standard automotive terminals operate from -40°C to +85°C, while marine applications may require -20°C to +80°C ranges. Always verify specifications for your specific environment.
How often should waterproof terminal connections be inspected?
Inspection frequency depends on application severity and safety criticality. Marine applications should be inspected annually, automotive systems every 2-3 years, and industrial applications based on maintenance schedules. Look for corrosion, looseness, or seal degradation during inspections.
Are there special considerations for aluminum wire connections?
Yes, aluminum wire requires terminals specifically designed for aluminum conductors or bimetallic designs that prevent galvanic corrosion. Use anti-oxidant compounds and ensure proper crimp pressure to break through aluminum oxide layers. Consider thermal expansion differences in connection design.
Conclusion and Expert Recommendations
Selecting the right waterproof cold-pressed terminals requires careful consideration of environmental conditions, electrical requirements, and long-term reliability needs. Prioritize terminals that meet or exceed your IP rating requirements, use high-quality sealing materials, and comply with relevant industry standards.
Key takeaways for optimal performance:
- Match terminal specifications exactly to your application requirements
- Use calibrated tools and follow manufacturer installation procedures
- Implement regular inspection schedules based on environmental severity
- Never compromise on quality for cost savings in critical applications
For complex installations or high-reliability applications, consult with certified electrical professionals who can verify proper selection, installation, and testing procedures. Proper terminal selection and installation directly impacts system safety, reliability, and long-term maintenance costs.
Professional Recommendation: When in doubt about terminal selection or installation requirements, engage qualified electrical engineers or certified technicians. The cost of professional consultation is minimal compared to system failure consequences in critical applications.