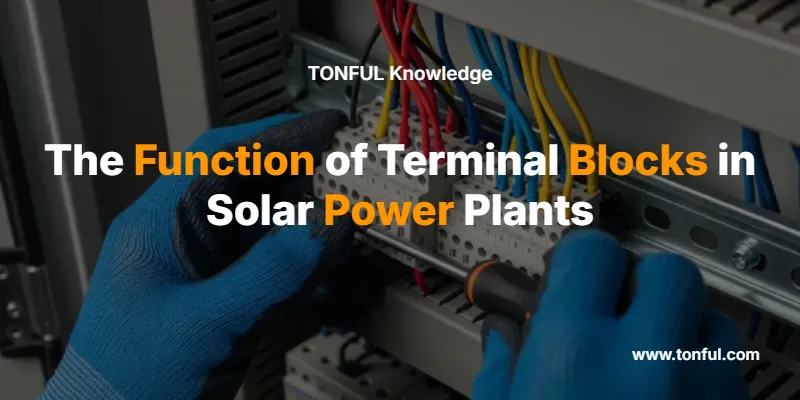
Terminal blocks in solar power plants serve as critical electrical connection points that safely join, distribute, and protect DC and AC circuits throughout the entire photovoltaic system. These essential components ensure reliable power transmission, enable systematic maintenance, and provide crucial safety isolation points that prevent electrical hazards and system failures.
What Are Terminal Blocks in Solar Power Plants?
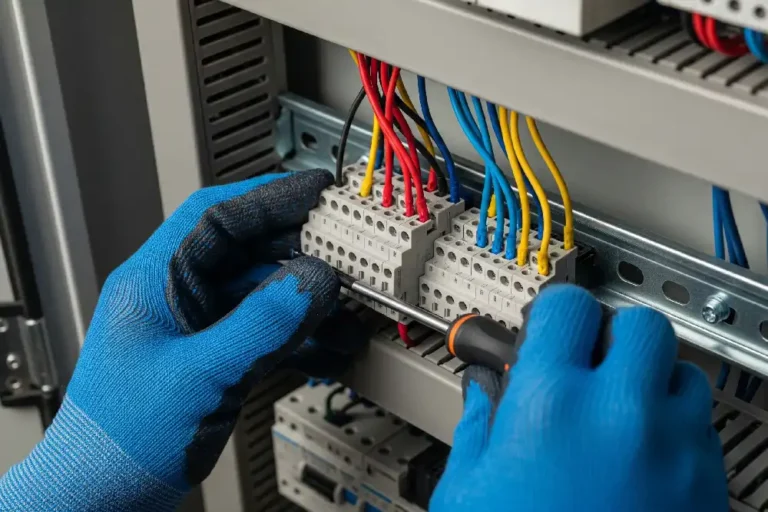

Terminal blocks are modular electrical connectors that create secure, organized connection points between different components in solar power systems. They function as central hubs where multiple wires meet, allowing electrical current to flow safely between solar panels, inverters, combiner boxes, monitoring systems, and grid connections.
Key Functions:
- Circuit organization: Group and separate different voltage levels and circuit types
- Connection security: Provide screw-terminal or spring-clamp connections stronger than wire nuts
- System accessibility: Enable easy maintenance and troubleshooting without rewiring
- Safety isolation: Create clear disconnection points for maintenance and emergency shutdowns
- Code compliance: Meet NEC Article 690 requirements for solar installations
Types of Terminal Blocks Used in Solar Power Plants
DC Terminal Blocks
| Terminal Block Type | Voltage Rating | Current Rating | Primary Use | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fused Terminal Blocks | 1000V DC | 20-100A | String combiner boxes | Built-in fuse protection, visual fault indication |
| Standard Rail Mount | 1000V DC | 15-50A | Junction boxes, control panels | DIN rail mounting, multiple connection points |
| High-Current Blocks | 1500V DC | 125-400A | Main DC combiners | Heavy-duty construction, IP65 rating |
| Ground Terminal Blocks | 1000V DC | 100A+ | Equipment grounding | Green marking, enhanced corrosion resistance |
AC Terminal Blocks
| Terminal Block Type | Voltage Rating | Current Rating | Primary Use | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neutral Blocks | 600V AC | 100-200A | AC disconnect panels | Blue marking, isolated from housing |
| Line Terminal Blocks | 600V AC | 50-150A | Inverter connections | Phase separation, arc-fault protection |
| Distribution Blocks | 480V AC | 200-600A | Main AC panels | Multi-tap design, UL listed |
Critical Functions of Terminal Blocks in Solar Systems
1. String Combining and Distribution
Terminal blocks in combiner boxes collect DC output from multiple solar panel strings, creating a single high-current connection to inverters. This consolidation reduces wiring complexity and creates accessible test points for system monitoring.
Safety Benefit: Fused terminal blocks protect individual strings from overcurrent conditions while maintaining system operation.
2. Grounding System Integration
Equipment grounding terminal blocks ensure all metallic components maintain proper electrical continuity to ground, preventing dangerous voltage buildup during fault conditions.
Code Requirement: NEC 690.43 mandates dedicated grounding terminal blocks for solar equipment grounding conductors.
3. AC and DC Circuit Separation
Terminal blocks provide physical and electrical separation between DC solar circuits and AC grid connections, preventing dangerous mixing of circuit types during installation and maintenance.
4. Monitoring System Connections
Specialized terminal blocks connect monitoring sensors, data loggers, and communication equipment throughout the solar plant, enabling real-time performance tracking and fault detection.
Selection Criteria for Solar Terminal Blocks
Essential Technical Specifications
Voltage Rating Requirements:
- 1000V DC minimum for standard solar string circuits
- 1500V DC for high-voltage utility installations
- 600V AC for grid-tie inverter connections
Current Rating Guidelines:
- Calculate maximum system current plus 25% safety margin
- Consider temperature derating factors for outdoor installations
- Account for future system expansion needs
Environmental Protection:
- IP65 rating minimum for outdoor combiner boxes
- UV-resistant housings for direct sunlight exposure
- Temperature range: -40°F to +185°F operating capability
Safety and Compliance Features
UL Listed Components:
- UL 1741 certification for grid-tie systems
- UL 98B rating for industrial control equipment
- UL 489 listing for circuit protection devices
Arc-Fault Protection:
- Built-in arc-fault detection capabilities
- Rapid disconnection under fault conditions
- Visual indication of fault status
Installation Best Practices for Solar Terminal Blocks
Step-by-Step Installation Process
1. Planning and Design Phase
- Calculate total system current requirements
- Select appropriate terminal block ratings with 25% margin
- Plan wire routing and access requirements
- Verify local code compliance requirements
2. Mounting Preparation
- Install DIN rails level and secure in approved enclosures
- Ensure adequate spacing between terminal blocks (minimum 6mm)
- Verify proper enclosure grounding connection
- Check environmental sealing integrity
3. Terminal Block Installation
- Mount blocks on DIN rail with proper orientation
- Install end plates and barriers between different circuits
- Verify secure mechanical attachment
- Install protective covers where required
4. Wiring Connections
- Strip wire insulation to manufacturer specifications (typically 10-12mm)
- Insert wires fully into terminal chambers
- Torque screw terminals to specified values (typically 7-12 in-lbs)
- Verify connection security with gentle pull test
5. System Testing and Documentation
- Perform continuity tests on all connections
- Measure insulation resistance between circuits
- Document terminal assignments and wire labeling
- Create as-built drawings for maintenance reference
Safety Warning: Electrical Hazards
DANGER: Solar panels produce lethal DC voltage even in low-light conditions. Always follow lockout/tagout procedures and use appropriate PPE. Installation must be performed by qualified electricians familiar with NEC Article 690 requirements.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Routine Maintenance Schedule
Quarterly Inspections:
- Visual inspection of terminal housings for damage
- Check connection tightness with calibrated torque driver
- Verify protective cover integrity
- Clean dust and debris from ventilation areas
Annual Maintenance:
- Thermographic inspection of all connections
- Insulation resistance testing between circuits
- Replacement of worn labels and documentation updates
- Corrosion assessment and treatment
Common Problems and Solutions
| Problem | Symptoms | Causes | Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Loose Connections | Hot spots, arcing sounds | Thermal cycling, vibration | Re-torque to specification, replace if damaged |
| Corrosion | White/green deposits, high resistance | Moisture ingress, dissimilar metals | Clean connections, apply approved anti-oxidant |
| Insulation Failure | Ground faults, arc faults | UV degradation, overheating | Replace affected terminal blocks, upgrade ratings |
| Contact Wear | Intermittent connections | High current cycling | Replace terminal blocks, verify proper sizing |
Expert Tips for Optimal Performance
Professional Recommendation: Use terminal blocks rated for at least 125% of maximum system current to account for temperature derating and future expansion needs.
Installation Tip: Apply dielectric grease to aluminum conductors before insertion into terminal blocks to prevent galvanic corrosion.
Maintenance Insight: Schedule thermographic inspections during peak solar production hours when connections carry maximum current, revealing developing problems before failure.
Compliance and Standards
National Electrical Code (NEC) Requirements
Article 690 – Solar Photovoltaic Systems:
- Section 690.31: Wiring methods and materials
- Section 690.43: Equipment grounding requirements
- Section 690.47: Grounding electrode system connections
Key Compliance Points:
- All terminal blocks must be listed for solar applications
- DC circuit connections require tool-opening or locked covers
- Grounding terminal blocks must be distinctly marked
- Working space clearances must be maintained per NEC 110.26
Industry Standards
UL Standards:
- UL 1741: Inverters and charge controllers
- UL 98B: Industrial control equipment
- UL 2703: Rack mounting systems
IEEE Standards:
- IEEE 1547: Interconnection standards
- IEEE 929: Utility interface requirements
Quick Reference: Terminal Block Selection Guide
For Residential Systems (≤10kW)
- Voltage Rating: 1000V DC minimum
- Current Rating: 20-40A per string
- Protection: Individual fused blocks recommended
- Enclosure: NEMA 3R outdoor rating
For Commercial Systems (10kW-1MW)
- Voltage Rating: 1000-1500V DC
- Current Rating: 50-125A per combiner
- Protection: Group fusing with monitoring
- Enclosure: NEMA 4X with ventilation
For Utility-Scale Systems (>1MW)
- Voltage Rating: 1500V DC standard
- Current Rating: 200-600A main combiners
- Protection: Integrated monitoring and control
- Enclosure: Walk-in buildings with HVAC
Frequently Asked Questions
What voltage rating do I need for terminal blocks in solar installations?
Most residential and commercial solar installations require terminal blocks rated for 1000V DC minimum. Utility-scale installations increasingly use 1500V DC systems for improved efficiency. Always verify your specific system voltage requirements before selection.
How do I know if my terminal blocks are properly sized?
Calculate the maximum current in each circuit and select terminal blocks rated for at least 125% of this value. For example, if your string current is 10A, choose terminal blocks rated for at least 12.5A. This provides safety margin for temperature derating and current variations.
Can I use standard electrical terminal blocks for solar applications?
No. Solar applications require terminal blocks specifically listed for photovoltaic use under UL standards. Standard terminal blocks may not handle the unique characteristics of DC power, UV exposure, and temperature cycling found in solar installations.
What maintenance do terminal blocks require in solar plants?
Perform quarterly visual inspections and annual thermographic scans. Check connection tightness annually using a calibrated torque driver. Clean debris from ventilation areas and verify protective cover integrity during each inspection.
How do I prevent corrosion in outdoor terminal block installations?
Use terminal blocks with appropriate IP ratings (IP65 minimum), apply approved anti-oxidant compound to aluminum connections, ensure proper enclosure sealing, and specify stainless steel or tin-plated hardware for corrosive environments.
What happens if a terminal block fails in a solar power plant?
Terminal block failure can cause string disconnection, reduced power output, or safety hazards. Modern systems include monitoring that detects connection problems. Failed blocks must be replaced immediately by qualified technicians following proper safety procedures.
Conclusion
Terminal blocks are fundamental safety and performance components in solar power plants, serving as critical connection points that organize, protect, and enable maintenance of complex electrical systems. Proper selection, installation, and maintenance of these components ensure reliable operation, code compliance, and personnel safety throughout the system’s 25+ year lifespan.
When selecting terminal blocks for your solar installation, prioritize appropriate voltage and current ratings, environmental protection, and compliance with NEC Article 690 requirements. Always consult with qualified electrical contractors familiar with solar installations to ensure proper system design and code compliance.
For complex utility-scale installations or specialized applications, consider engaging certified solar system designers who can optimize terminal block selection for your specific operational requirements and environmental conditions.