Introduction
Every year, electrical failures cost fleet operators millions in downtime, emergency repairs, and safety incidents. A single blown fuse can strand a heavy-duty truck on the highway, delay critical deliveries, and damage your company’s reputation. Yet many fleet managers and technicians still struggle with a fundamental question: should you use a Standard or Maxi blade fuse for a specific circuit?
Proper fuse selection isn’t just about matching amperage ratings. It’s about understanding the electrical demands of modern truck systems, thermal management requirements, and the critical differences between fuse types. Standard blade fuses excel in low-current accessory circuits, while Maxi blade fuses provide robust protection for high-amperage motor and power distribution systems.
This comprehensive guide will help you make informed decisions about blade fuse selection for heavy-duty truck electrical repair. You’ll learn the technical specifications, applications, and critical differences that determine which fuse type belongs in each circuit of your fleet vehicles.

What Are Blade Fuses?
Blade fuses are circuit protection devices that prevent electrical damage by breaking the circuit when current exceeds safe levels. Unlike the fragile glass tube fuses they replaced, blade fuses feature a durable plastic housing with two metal prongs that plug directly into fuse holders.
Littelfuse introduced the automotive blade fuse in 1976, revolutionizing vehicle electrical protection. This innovation addressed the chronic problems of glass fuses: poor vibration resistance, difficult handling, and inconsistent performance in automotive environments. The blade design provided superior mechanical stability and reliable electrical contact.
The basic blade fuse consists of three critical components. The plastic housing provides physical protection and allows for safe handling while incorporating a standardized color-coding system for quick amperage identification. Inside the housing, a zinc alloy fuse element carries the rated current indefinitely but melts rapidly when overcurrent occurs. The copper or zinc-plated blade terminals ensure low-resistance connections in the fuse holder.
This simple yet effective design has become the industry standard for automotive fuse applications. Modern vehicles and heavy-duty trucks rely on blade fuses to protect everything from interior lights to critical engine management systems. Understanding the different types of blade fuses is essential for proper circuit protection in commercial vehicle maintenance.
Standard Blade Fuses (ATO/ATC) Overview
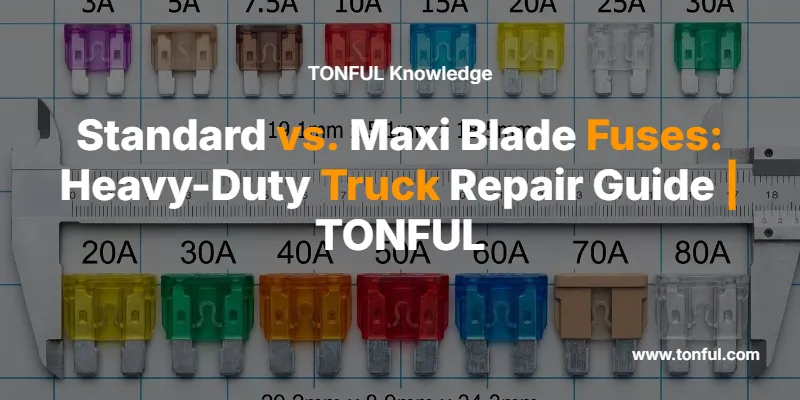
Standard blade fuses, also designated as ATO or ATC fuses, measure 19.1mm wide × 18.5mm high × 5.1mm thick. These dimensions have remained consistent since their introduction, ensuring universal compatibility across vehicle manufacturers and fuse holder designs. The Standard blade fuse serves as the backbone of automotive electrical protection.
The amperage range for Standard blade fuses spans from 1A to 40A, with voltage ratings of 32V DC. This range covers most accessory and control circuits in heavy-duty trucks. Common amperage ratings include 2A, 3A, 5A, 7.5A, 10A, 15A, 20A, 25A, 30A, 35A, and 40A, each identified by a specific color code.

You’ll encounter two variants of Standard blade fuses: ATO and ATC. The ATO (Automotive Fuse – Open Element) features an opening at the bottom that exposes the fuse element between the blades. The ATC (Automotive Fuse – Closed Element) has a fully sealed plastic body that protects the element from moisture, vibration, and potential shorts. ATC fuses are now the predominant choice for their superior environmental protection.
In heavy-duty trucks, Standard blade fuses protect numerous circuits:
- Interior and exterior lighting systems
- Windshield wiper motors
- HVAC control modules
- Radio and communication equipment
- Instrument cluster displays
- Power window motors
- Door lock actuators
- Electronic control modules
The advantages of Standard blade fuses include widespread availability, low cost, and compact size that saves space in fuse panels. However, they have limitations. The relatively thin fuse element and smaller blade cross-section restrict their current-carrying capacity. Standard fuses aren’t suitable for high-current applications like starter circuits or alternator protection, where thermal management becomes critical. For more information about different blade fuse types, visit our comprehensive guide on automotive blade fuse types.
Maxi Blade Fuses Overview
Maxi blade fuses, designated as APX, are substantially larger than their Standard counterparts, measuring 29.2mm wide × 34.3mm high × 8.9mm thick. This increased size isn’t merely cosmetic; it provides critical performance advantages for high-current applications. The Maxi blade fuse represents the heavy-duty solution for commercial vehicle electrical systems.
The amperage range for Maxi fuses spans from 20A to 120A, with voltage ratings from 32V to 58V DC depending on the specific fuse design. This expanded capacity makes them essential for power-hungry circuits in modern heavy-duty trucks. Common ratings include 20A, 25A, 30A, 40A, 50A, 60A, 70A, 80A, 100A, and 120A.
A key technological feature of Maxi fuses is diffusion pill technology. This engineering innovation provides time-delayed or “slow-blow” protection, allowing the fuse to withstand brief overcurrent surges without nuisance blowing. This characteristic is crucial for motor-powered applications that generate large inrush currents during startup but operate normally once running.

The thicker fuse element and wider blade terminals provide superior heat dissipation, preventing premature failure in sustained high-current conditions. The increased thermal mass allows the fuse to carry rated current indefinitely while maintaining stable operating temperatures.
Common applications for Maxi blade fuses in heavy-duty trucks include:
- Starter motor circuits (handling 100-150A inrush currents)
- Alternator output protection (70-100A continuous)
- Main power distribution feeds
- Electric cooling fan motors (40-80A)
- Hydraulic pump systems
- Air conditioning compressors
- Power inverter circuits
- Auxiliary power outlets
- Battery management systems
The primary advantage of Maxi fuses is their ability to protect high-power circuits without nuisance tripping. The larger physical size accommodates more robust internal components that withstand both electrical and thermal stress. However, Maxi fuses require larger fuse holders and panel space, which can be a constraint in compact electrical systems. They also cost more than Standard fuses due to increased material requirements and specialized manufacturing processes.
For fleet maintenance operations, understanding when to specify Maxi blade fuses is critical for system reliability and longevity. Using an undersized Standard fuse in a high-current circuit will result in frequent failures, while using an oversized fuse eliminates proper circuit protection.
Direct Comparison: Standard vs. Maxi Blade Fuses
Understanding the technical differences between Standard and Maxi blade fuses is essential for proper circuit protection in heavy-duty truck repair. This detailed comparison will help you select the appropriate fuse type for every application.
Technical Specifications Comparison
| Feature | Standard (ATO/ATC) | Maxi (APX) |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Dimensions | 19.1mm × 18.5mm × 5.1mm | 29.2mm × 34.3mm × 8.9mm |
| Amperage Range | 1A to 40A | 20A to 120A |
| Voltage Rating | 32V DC | 32V to 58V DC |
| Typical Applications | Lights, wipers, HVAC controls, radio, accessories | Starter circuits, alternators, power distribution, cooling fans |
| Blade Thickness | 0.8mm | 1.5mm |
| Heat Dissipation | Moderate (suitable for steady-state loads) | Excellent (handles high thermal loads) |
| Response Time | Fast-acting (immediate protection) | Time-delayed (tolerates inrush currents) |
| Cost per Unit | $0.50 – $1.50 | $2.00 – $5.00 |
| Availability | Universal (every auto parts store) | Common (truck supply dealers) |
| Installation | Standard fuse panels | Requires larger fuse holders |

Thermal Management Differences
The physical size difference between these fuse types directly impacts their thermal performance. A Standard 30A blade fuse has approximately 95 square millimeters of surface area for heat dissipation. A Maxi 30A fuse provides over 250 square millimeters of surface area—more than 2.5 times greater cooling capacity.
This thermal advantage becomes critical in continuous high-current applications. A truck’s cooling fan motor might draw 35A continuously during summer highway driving. A Standard 40A fuse would operate near its thermal limits, potentially failing prematurely due to heat stress. A Maxi 40A or 50A fuse handles this load comfortably within its design parameters.
Inrush Current Handling
Motor circuits present a unique challenge for circuit protection. Electric motors can draw 5-8 times their normal operating current during the first fraction of a second at startup. A hydraulic pump motor with a 25A running current might spike to 150-200A momentarily.
Standard blade fuses use fast-acting elements designed to blow quickly when overcurrent occurs. This rapid response protects sensitive electronics but can cause nuisance tripping with motor loads. Maxi fuses incorporate diffusion pill technology that delays the thermal response, allowing brief overcurrent surges without opening the circuit. This makes them ideal for motor-powered applications in heavy-duty trucks.
When to Use Each Type
Choose Standard blade fuses for:
- Lighting circuits (headlights, taillights, interior lights)
- Control circuits (instrument clusters, control modules)
- Low-power accessories (radio, USB ports, 12V outlets)
- Electronic components (sensors, actuators, displays)
- Any circuit drawing less than 20A continuously
Choose Maxi blade fuses for:
- Starter motor circuits
- Alternator output protection
- Main battery distribution feeds
- Electric cooling fans and HVAC blowers
- Air compressor motors
- Hydraulic system pumps
- High-power auxiliary circuits
- Any circuit requiring more than 40A protection
The overlap zone between 20A and 40A requires careful consideration. If the circuit involves a motor with high inrush current, specify a Maxi fuse. For steady-state loads like lighting or heaters, a Standard fuse suffices. For additional guidance on selecting between different blade fuse sizes, review our Standard vs. Mini blade fuse comparison.
Never substitute a Standard fuse for a specified Maxi fuse, even at the same amperage rating. The physical differences mean they’re not interchangeable, and using the wrong type can lead to premature failure or inadequate circuit protection.
Color-Coding System
The automotive industry uses a standardized color-coding system to enable quick identification of blade fuse amperage ratings. However, a critical distinction exists: the same color can indicate different amperage ratings depending on whether you’re examining a Standard or Maxi blade fuse. Understanding this difference prevents dangerous misidentification during repairs.
Standard Blade Fuse Color Codes
| Color | Amperage | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Gray | 2A | Parking lights, license plate lights |
| Violet | 3A | Interior courtesy lights |
| Tan/Brown | 5A | Instrument panel lights |
| Brown | 7.5A | Radio memory, clock |
| Red | 10A | Radio, power mirrors |
| Blue | 15A | Power windows, sunroof |
| Yellow | 20A | Horn, cigarette lighter |
| Clear/Natural | 25A | Power seats, windshield washer |
| Green | 30A | Electric radiator fan |
| Orange | 40A | Electric defogger, fuel pump |
Maxi Blade Fuse Color Codes
| Color | Amperage | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Yellow | 20A | Auxiliary power circuits |
| Clear/Natural | 25A | Low-power distribution feeds |
| Green | 30A | Cooling fan circuits |
| Orange | 40A | HVAC blower motors |
| Red | 50A | Battery charging circuits |
| Blue | 60A | Alternator output protection |
| Tan/Brown | 70A | Main power distribution |
| Clear/Natural | 80A | Starter circuit protection |
| Clear/Natural | 100A | High-capacity power feeds |

Critical Color-Coding Warnings
Notice that yellow indicates 20A in both Standard and Maxi fuses, but red means 10A in Standard fuses and 50A in Maxi fuses. This five-fold difference in amperage for the same color creates a significant safety hazard if you confuse the fuse types. Similarly, green represents 30A in both categories, while blue indicates 15A for Standard but 60A for Maxi fuses.
Always read the amperage rating printed on the top of the fuse. Never rely solely on color identification, especially when working with mixed Standard and Maxi fuse systems. The printed number is the definitive specification. For detailed information about reading fuse labels and color codes, consult our guide on how to read automotive blade fuse labels.
Some manufacturers produce clear or natural-colored fuses in multiple amperage ratings for both Standard and Maxi types. These fuses rely entirely on printed markings for identification, making visual inspection under the hood challenging. Always remove suspect fuses for close examination in proper lighting.
Color-Coding Best Practices
When performing fleet maintenance:
- Separate Storage: Keep Standard and Maxi fuses in clearly labeled containers to prevent mixing
- Verify Markings: Always confirm the printed amperage before installation
- Update Labels: If you replace fuses, update fuse box labels immediately
- Train Technicians: Ensure all maintenance personnel understand color code variations
- Stock by Color: Organize your fuse inventory by color within each size category
For comprehensive information about blade fuse amperage ratings and color codes, refer to industry standards and manufacturer specifications. Understanding this color-coding system improves repair speed, reduces errors, and enhances electrical system safety in your heavy-duty truck fleet.
Industry Standards & Certifications
Professional blade fuse manufacturers comply with rigorous international standards that govern dimensional specifications, performance characteristics, and testing protocols. These standards ensure product interchangeability, reliability, and safety across the global automotive supply chain.
SAE J1284 Standard
The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) J1284 standard, “Blade Type Electric Fuses,” establishes the foundational requirements for automotive blade fuses used in North American vehicles. This standard specifies physical dimensions, electrical performance parameters, and environmental durability requirements. It covers all blade fuse types including Standard (ATO/ATC) and Maxi (APX) configurations.
SAE J1284 mandates specific temperature cycling tests, vibration resistance protocols, and current-carrying capacity verification. Fuses must demonstrate stable performance across operating temperatures from -40°C to +125°C, reflecting the extreme conditions trucks encounter from Arctic winter operations to desert summer heat.
ISO 8820 Series
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 8820 series, “Road vehicles — Fuses,” provides globally recognized standards that harmonize automotive fuse specifications worldwide. Different parts of this multi-section standard address specific fuse types:
- ISO 8820-3: Blade-type fuses (Standard ATO/ATC fuses)
- ISO 8820-4: Maxi fuses (high-current blade fuses)
- ISO 8820-5: Bolt-in type fuses (heavy-duty applications)
These standards define precise dimensional tolerances, ensuring that fuses from any compliant manufacturer fit properly in any standard fuse holder. For example, ISO 8820-3 specifies that Standard blade fuses must measure 19.1mm (±0.2mm) in width, guaranteeing universal compatibility.
ISO 8820 also establishes performance requirements including:
- Minimum time-to-blow characteristics at specified overcurrent levels
- Maximum voltage drop at rated current
- Resistance to mechanical shock and vibration
- Terminal pull-out force requirements
- Ambient temperature derating factors
Compliance Importance
For fleet operators and procurement managers, purchasing fuses from ISO 8820 and SAE J1284 certified manufacturers provides several critical advantages:
Quality Assurance: Standards compliance indicates the manufacturer follows proper quality control processes and testing protocols. You receive consistent product performance batch after batch.
OEM Compatibility: Original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) design vehicle electrical systems around standardized fuse specifications. Using compliant fuses ensures proper fit and function without modification.
Insurance Requirements: Many commercial vehicle insurance policies require the use of standards-compliant replacement parts. Non-compliant fuses could void coverage in the event of an electrical fire or system failure.
Legal Liability: In accident investigations involving electrical failures, documentation of standards-compliant parts provides important protection. Using substandard or non-compliant fuses could create legal liability.
Warranty Protection: Vehicle manufacturer warranties typically require the use of compliant replacement parts. Installing non-standard fuses may void electrical system warranties.
As a professional blade fuse manufacturer, TONFUL Electric ensures all products meet or exceed these international standards. Third-party testing laboratories verify compliance through rigorous testing programs. When you specify standards-compliant blade fuses for your fleet, you’re investing in proven reliability and regulatory compliance that protects both your vehicles and your business.
Troubleshooting & Replacement Guidelines
Proper blade fuse diagnosis and replacement procedures are essential skills for maintaining heavy-duty truck electrical systems. Following systematic troubleshooting methods saves time, prevents repeat failures, and ensures safe repairs.
How to Test a Blade Fuse with a Multimeter
Testing a blade fuse with a multimeter provides definitive confirmation of fuse condition. Follow these steps:
- Set Your Multimeter: Switch the multimeter to the continuity test mode (often indicated by a speaker/sound wave symbol) or the lowest resistance range (typically 200Ω)
- Remove the Fuse: Always remove the fuse from its holder before testing. Testing in-circuit can provide misleading results due to parallel paths
- Test the Fuse: Touch one multimeter probe to each blade terminal. A good fuse will show continuity (multimeter beeps) or near-zero resistance (typically <0.1Ω). A blown fuse shows infinite resistance (OL or Open Line on the display)
- Visual Inspection: Look through the transparent plastic housing. A blown fuse element shows a visible gap or burn mark in the metal strip
For detailed testing procedures and diagnostic techniques, refer to our guide on how to test a blade fuse with a multimeter.
Signs of a Blown Fuse
Recognizing blown fuse symptoms accelerates troubleshooting:
- Complete loss of function in specific circuits (lights, wipers, accessories)
- Multiple related systems failing simultaneously
- Intermittent operation that becomes permanent failure
- Visible burn marks or discoloration on the fuse body
- Melted or deformed plastic housing
- Metallic smell from fuse panel area
Common Causes of Fuse Failure in Trucks
Understanding failure causes prevents repeat problems:
Overcurrent from Short Circuits: Damaged wiring insulation allows current to bypass the load, creating excessive current flow. Road debris, chafed harnesses, or pinched wires commonly cause shorts in truck electrical systems.
Overloaded Circuits: Adding aftermarket accessories without proper circuit analysis can exceed fuse capacity. LED light bars, auxiliary heaters, or power inverters often overload existing circuits.
Moisture Intrusion: Water entering fuse boxes or corroded terminals increases resistance, generating heat that degrades fuse elements. This particularly affects trucks operating in wet environments or those with compromised weatherseals.
Mechanical Vibration: Heavy-duty trucks experience constant vibration that can fatigue fuse elements over time. While rare with quality fuses, inferior products may fail from mechanical stress alone.
Age Degradation: Fuse elements oxidize over years of service, increasing resistance and reducing current-carrying capacity. Replace fuses that show any signs of corrosion or discoloration.
Wrong Fuse Rating: Using a higher-rated fuse than specified eliminates proper circuit protection. The fuse won’t blow before wiring overheats, creating fire hazards.
Step-by-Step Replacement Procedure
Follow this systematic approach for safe fuse replacement:
- Identify the Problem Circuit: Use the vehicle’s fuse diagram to locate the correct fuse. Fuse box covers typically include circuit identification charts.
- Disconnect Power: Turn off the ignition and remove the key. For circuits connected directly to the battery, disconnect the negative battery terminal.
- Remove the Blown Fuse: Use fuse pullers (never metal tools) to extract the fuse. Needle-nose pliers can damage fuse blades or create shorts.
- Inspect the Fuse and Holder: Check for signs of overheating, corrosion, or physical damage. Clean corroded fuse holder terminals with electrical contact cleaner.
- Install the Correct Replacement: Verify the new fuse matches the required amperage rating. Push firmly but don’t force the fuse into the holder.
- Test the Circuit: Reconnect power and verify proper operation. If the new fuse blows immediately, you have an active short circuit that requires professional diagnosis.
- Document the Repair: Note the fuse replacement in maintenance records, including date, location, and any observations about the cause.
Critical Safety Precautions
Never compromise these safety requirements:
- Never Use Higher-Rated Fuses: Installing a 30A fuse in a circuit designed for 20A eliminates protection. The wiring will overheat before the fuse blows, creating fire risk.
- Never Use Temporary Bypasses: Some technicians use wire, foil, or coins to bypass blown fuses. This eliminates all circuit protection and can cause catastrophic electrical fires.
- Address Repeat Failures: If a fuse blows repeatedly, stop and diagnose the underlying problem. Repeated replacement without fixing the cause creates safety hazards.
- Use Quality Fuses Only: Counterfeit or substandard fuses may not meet performance specifications. Purchase from reputable automotive fuse manufacturers that comply with SAE and ISO standards.
For guidance on when replacement is necessary versus when further diagnosis is required, see our article on when to replace a blown blade fuse.
TONFUL’s Blade Fuse Solutions
TONFUL Electric manufactures premium automotive blade fuses engineered specifically for demanding heavy-duty truck applications. As a professional blade fuse manufacturer, we understand that fleet reliability depends on the quality of every electrical component.
Manufacturing Standards
Our blade fuses meet or exceed all international standards including SAE J1284 and ISO 8820 specifications. Each production batch undergoes rigorous testing protocols:
- Dimensional Verification: Automated inspection systems verify blade spacing, housing dimensions, and terminal specifications to ensure universal compatibility
- Electrical Testing: Every fuse rating is tested at 100%, 110%, and 135% of rated current to verify proper time-current characteristics
- Temperature Cycling: Random samples endure -40°C to +125°C temperature cycles to validate environmental performance
- Vibration Testing: Accelerated vibration testing simulates years of truck operation to verify mechanical durability
- Pull-Out Force Testing: Terminal retention testing ensures fuses remain secure in holders despite constant vibration
Product Range
TONFUL’s blade fuse catalog includes comprehensive coverage for heavy-duty truck applications:
Standard Blade Fuses (ATO/ATC):
- Complete amperage range: 1A, 2A, 3A, 5A, 7.5A, 10A, 15A, 20A, 25A, 30A, 35A, 40A
- ATC closed-element design for superior environmental protection
- Standard industry color-coding for rapid identification
- Transparent housing for visual element inspection
Maxi Blade Fuses (APX):
- Heavy-duty range: 20A, 25A, 30A, 40A, 50A, 60A, 70A, 80A, 100A, 120A
- Diffusion pill technology for time-delayed protection
- Enhanced heat dissipation for continuous high-current applications
- Rated for both 32V and 58V systems
Bulk Purchasing for Fleet Maintenance
Fleet operators benefit from TONFUL’s bulk purchasing programs designed specifically for commercial vehicle maintenance operations:
- Volume Discounts: Significant cost savings on orders exceeding 1,000 pieces
- Custom Packaging: Fuses packed in maintenance-friendly configurations
- Consistent Supply: Guaranteed stock availability of all common ratings
- Rapid Fulfillment: Expedited shipping for emergency replacements
- Technical Support: Direct access to engineering team for application questions
Custom Assortment Kits
TONFUL offers pre-configured assortment kits optimized for different vehicle types and maintenance scenarios:
Heavy-Duty Truck Kit: 200-piece assortment featuring commonly needed Standard and Maxi fuses for Class 7-8 trucks
Fleet Emergency Kit: Compact 50-piece selection of critical fuse ratings for roadside repairs
Shop Stock Kit: 500-piece master assortment for full-service truck maintenance facilities
Custom Configurations: We design custom assortment kits based on your fleet’s specific electrical system requirements and historical usage patterns
Quality Control and Testing
TONFUL’s quality management system ensures every fuse meets exacting standards:
- ISO 9001:2015 certified manufacturing facility
- Statistical process control (SPC) monitoring of critical dimensions
- Automated optical inspection (AOI) of fuse elements
- Third-party laboratory testing for standards compliance
- Traceability systems tracking every production batch
Our commitment to quality extends beyond manufacturing. TONFUL provides comprehensive technical documentation including:
- Detailed electrical specifications and performance curves
- Installation and handling guidelines
- Application engineering support
- Failure analysis assistance for troubleshooting
When you choose TONFUL blade fuses for your heavy-duty truck fleet, you’re partnering with a manufacturer that understands the critical importance of electrical system reliability. Our products protect your vehicles, your drivers, and your business operations. Contact our B2B sales team to discuss your fleet’s specific requirements and discover how TONFUL’s blade fuse solutions can improve your maintenance efficiency and reduce electrical-related downtime.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I replace a Standard fuse with a Maxi fuse of the same amperage?
No, you cannot directly substitute a Standard blade fuse with a Maxi blade fuse even if they share the same amperage rating. The physical dimensions differ significantly: Standard fuses measure 19.1mm × 18.5mm while Maxi fuses measure 29.2mm × 34.3mm. They require different fuse holder designs and are not mechanically compatible. Additionally, Maxi fuses incorporate time-delay characteristics that Standard fuses lack, meaning they respond differently to overcurrent conditions. Always use the fuse type specified by the vehicle manufacturer for each circuit.
Why does my truck use different fuse sizes?
Heavy-duty trucks use different blade fuse sizes because electrical circuits have vastly different power requirements and operational characteristics. Low-current accessory circuits like interior lighting or radio systems need only 5-15A protection, making Standard blade fuses ideal. High-current circuits like starter motors or alternator outputs require 60-120A protection with thermal management capabilities that only Maxi fuses can provide. Using appropriately sized fuses for each circuit ensures optimal protection without wasting space or money on unnecessarily large components. The fuse size directly correlates to the circuit’s current demands and the heat dissipation requirements.
How do I know if I need a slow-blow or fast-acting fuse?
Determine fuse characteristics based on the circuit’s load type. Fast-acting fuses suit resistive loads (lights, heaters) that draw steady current without surge. Motor circuits require slow-blow (time-delay) fuses to tolerate startup inrush currents that can reach 5-8 times normal running current. Most Standard blade fuses are fast-acting, while Maxi fuses typically incorporate time-delay technology through diffusion pill design. Check the vehicle’s electrical schematic or service manual, which specifies fuse characteristics for each circuit. If documentation is unavailable, motor-powered circuits (fans, pumps, compressors) generally need time-delay protection, while lighting and electronic circuits require fast-acting fuses.
What causes repeated fuse failures in the same circuit?
Repeated fuse failures indicate an underlying electrical problem that requires diagnosis, not just continued fuse replacement. Common causes include: short circuits from damaged wiring insulation, overloaded circuits from excessive accessory additions, failing motors or actuators drawing excessive current, corroded connections creating high resistance and heat, loose terminals causing intermittent shorts, or moisture intrusion into electrical components. Using incorrect fuse ratings also causes repeat failures—either the fuse is too small for the circuit’s normal operation, or it’s too large and another component fails first. Professional electrical diagnosis with proper test equipment identifies the root cause. Never simply install progressively higher-rated fuses to “solve” the problem.
Are Maxi fuses better than Standard fuses?
Neither fuse type is universally “better”—they’re engineered for different applications. Maxi fuses excel in high-current circuits requiring superior thermal management and time-delay characteristics. Their larger size provides better heat dissipation and handles motor inrush currents effectively. However, Standard fuses are superior for low-current circuits where compact size, fast-acting protection, and lower cost matter most. Installing a Maxi fuse where a Standard fuse belongs wastes money and space while potentially providing slower-than-optimal overcurrent response. The “best” fuse is the one that matches the circuit’s electrical and thermal requirements as specified by the vehicle manufacturer. For more details about the differences between blade fuses and older designs, see our comparison guide on blade fuses vs. glass fuses.
Can I use automotive blade fuses in marine applications?
While automotive blade fuses meet SAE and ISO standards for vehicle use, marine environments present additional challenges including constant moisture exposure, salt spray, and more severe vibration. Many marine applications specify fuses meeting additional standards for water resistance and corrosion protection. Standard blade fuses can work in protected marine electrical panels, but exposed locations require waterproof fuse holders and potentially sealed fuse types. Maxi fuses with their larger size and robust construction often perform better in marine environments than Standard fuses. However, consult marine electrical codes and insurance requirements before substituting automotive fuses in boat applications. Some jurisdictions mandate marine-rated components for safety and insurance compliance.
How long do blade fuses last?
Quality blade fuses have no definite lifespan when properly applied and not subjected to overcurrent conditions. A correctly rated fuse protecting a normally functioning circuit can last the lifetime of the vehicle. However, several factors affect longevity: environmental exposure to heat, humidity, and vibration gradually degrades fuse elements; repeated thermal cycling from circuits near their rated capacity stresses the fuse element; corrosion from moisture or road salt increases resistance; and poor fuse holder contact adds stress. Inspect fuses annually during routine maintenance, particularly in harsh operating environments. Replace any fuse showing signs of corrosion, discoloration, or physical damage even if it hasn’t blown. For fleet maintenance, proactive replacement during major service intervals prevents roadside failures.
Conclusion
Selecting the appropriate blade fuse type for heavy-duty truck electrical repair requires understanding the fundamental differences between Standard and Maxi fuses. Standard blade fuses (ATO/ATC) excel in low-current accessory and control circuits from 1A to 40A, providing fast-acting protection in a compact package. Maxi blade fuses (APX) deliver robust high-current protection from 20A to 120A with time-delay characteristics essential for motor circuits and power distribution systems.
The key selection criteria include circuit current requirements, load characteristics (resistive versus inductive), thermal management needs, and physical space constraints. Never substitute fuse types based solely on matching amperage ratings—the physical dimensions, thermal properties, and response characteristics differ significantly. Always specify the fuse type designated by the vehicle manufacturer or follow proper electrical engineering principles when designing custom circuits.
For fleet operators, procurement managers, and maintenance technicians, investing in quality blade fuses from reputable manufacturers ensures electrical system reliability and reduces costly downtime. TONFUL Electric’s comprehensive range of Standard and Maxi blade fuses meets international standards and provides the performance heavy-duty trucks demand.
Contact TONFUL’s technical team today to discuss your specific fleet requirements, request bulk pricing for maintenance operations, or explore custom assortment kits designed for your vehicles. Proper fuse selection protects your trucks, your drivers, and your business operations—don’t compromise on this critical safety component.