Direct Answer: A stainless steel zip tie tool is used to install heavy-duty stainless steel cable ties by threading the tie through the tool’s feed slot, positioning it around your bundle, threading the tail through the locking head, and operating the tool’s tensioning and cutting mechanism to achieve proper tightness and create a clean, professional installation.
Understanding how to properly use a stainless steel zip tie tool is essential for anyone working with heavy-duty bundling applications, marine environments, or industrial installations where standard plastic ties simply won’t withstand the environmental demands.
What is a Stainless Steel Zip Tie Tool?
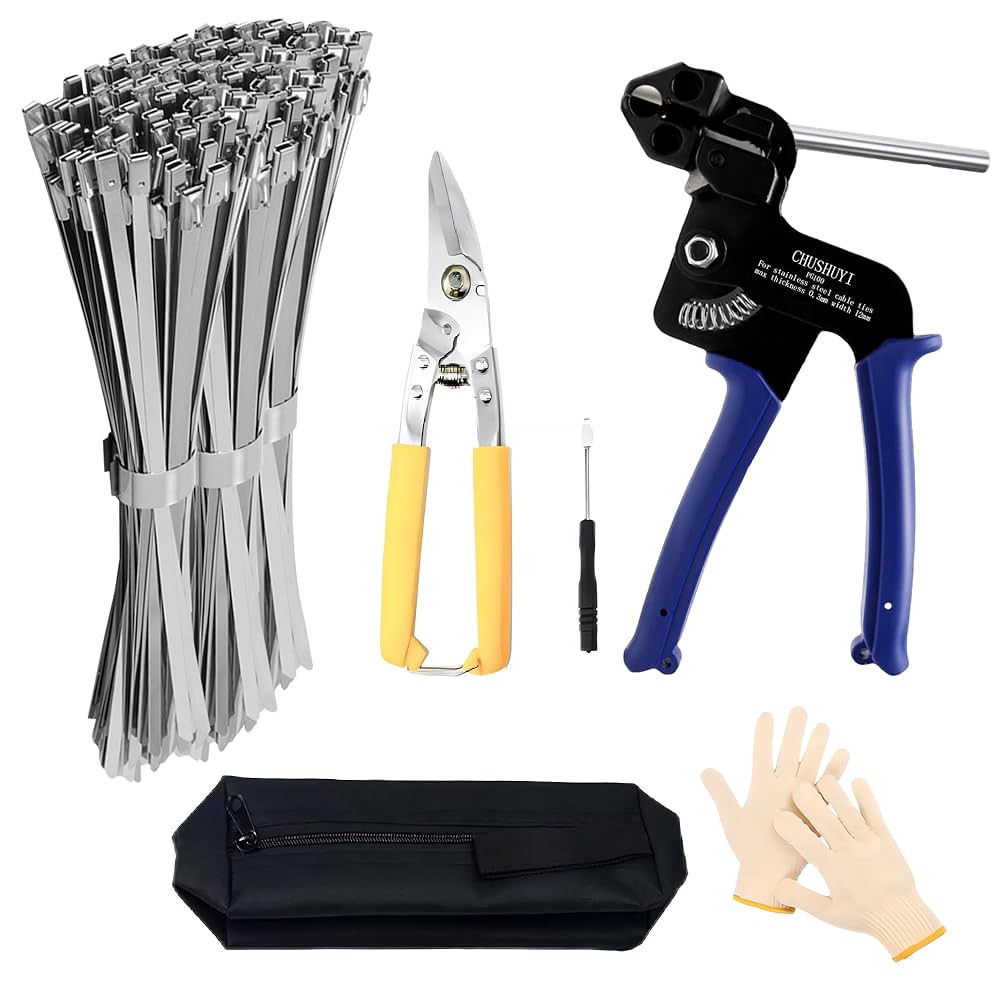

A stainless steel zip tie tool is a specialized manual or pneumatic installation device designed specifically for installing stainless steel cable ties (also called stainless steel zip ties or metal cable ties). Unlike standard zip tie installation tools, these tools are engineered to handle the increased strength requirements and precise tension control needed for metal cable tie installations.
Key Components of Stainless Steel Zip Tie Tools:
- Feed slot: Guides the stainless steel tie during installation
- Tensioning mechanism: Applies consistent, controlled tension
- Cutting blade: Creates clean, safe cuts without sharp edges
- Tension adjustment: Controls maximum applied force
- Handle system: Ergonomic grip for operator comfort and control
Manual vs. Pneumatic Stainless Steel Zip Tie Tools: Complete Comparison
| Feature | Manual Tools | Pneumatic Tools |
|---|---|---|
| Tension Control | 15-80 lbs typical | 18-175 lbs adjustable |
| Installation Speed | 10-15 ties per minute | 25-40 ties per minute |
| Operator Fatigue | Moderate after 50+ ties | Minimal even with 200+ ties |
| Initial Cost | $150-$400 | $800-$2,500 |
| Portability | Excellent (2-4 lbs) | Limited (requires air compressor) |
| Precision | Good with experience | Excellent and repeatable |
| Maintenance | Minimal | Regular lubrication required |
| Best Applications | Small batches, field work | Production environments |
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Use a Manual Stainless Steel Zip Tie Tool
Preparation Phase
- Select proper tie size – Match tie width to tool specifications (typically 1/4″, 3/8″, or 1/2″)
- Inspect the tool – Check feed slot for damage and ensure cutting blade is sharp
- Adjust tension setting – Set appropriate tension for your application (typically 15-25 lbs for electronics, 40-60 lbs for mechanical assemblies)
⚠️ Safety Warning: Always wear safety glasses when operating stainless steel zip tie tools. Metal fragments can be ejected during cutting operations.
Installation Process
Step 1: Load the Cable Tie
- Insert stainless steel tie tail into the tool’s feed slot
- Push tie through until approximately 2 inches protrudes from the front
- Ensure tie lies flat in the feed groove without twisting
Step 2: Position Around Bundle
- Wrap the tie around your cable bundle or application
- Keep bundle tight and organized during positioning
- Avoid crossing or overlapping cables unnecessarily
Step 3: Thread Through Locking Head
- Insert tie tail through the locking mechanism on the tie head
- Pull approximately 1-2 inches of tail through the head
- Ensure proper engagement with locking teeth
Step 4: Begin Tensioning
- Position tool handle perpendicular to the tie direction
- Squeeze handle slowly and steadily to engage tensioning mechanism
- Monitor bundle compression to avoid over-tightening
Step 5: Complete Installation
- Continue squeezing until tool reaches preset tension limit
- Tool will automatically stop applying force at proper tension
- Maintain pressure while cutting mechanism activates
Step 6: Final Cut and Inspection
- Tool automatically cuts excess tail flush with locking head
- Release handle pressure completely
- Inspect installation for proper tightness and clean cut edge
Applications and Use Cases for Stainless Steel Zip Tie Tools

Marine and Coastal Applications
- Boat wiring harnesses: Salt water environments require corrosion-resistant fastening
- Dock electrical systems: Exposure to spray and humidity demands metal ties
- Navigation equipment mounting: Vibration and weather resistance critical
Industrial Manufacturing
- Control panel assembly: High-temperature environments where plastic fails
- Automotive underhood: Heat and chemical exposure applications
- Food processing equipment: Washdown requirements and sanitary compliance
Telecommunications and Data Centers
- Outdoor fiber optic installations: UV and temperature cycling resistance
- Server rack cable management: Fire safety requirements in data centers
- Cell tower installations: Wind load and weather exposure demands
Chemical and Process Industries
- Pipe and conduit bundling: Chemical resistance requirements
- Explosion-proof installations: Fire safety and electrical codes compliance
- High-temperature applications: Where plastic ties would degrade
Expert Selection Criteria: Choosing the Right Stainless Steel Zip Tie Tool
Critical Decision Factors
Volume Requirements
- Low volume (< 50 ties/day): Manual tools provide cost-effective solution
- Medium volume (50-200 ties/day): Consider ergonomic manual or entry-level pneumatic
- High volume (200+ ties/day): Pneumatic tools essential for productivity and operator comfort
Application Environment
- Field installations: Manual tools offer portability advantage
- Shop/factory settings: Pneumatic tools with air supply provide superior performance
- Confined spaces: Compact manual tools necessary for accessibility
Tie Size Range Requirements
- Single size applications: Dedicated single-width tools offer best value
- Multiple tie widths: Adjustable tools provide versatility but cost more
- Heavy-duty applications: Ensure tool rated for maximum tie width and tension
Professional Quality Indicators
| Quality Factor | Good | Better | Best |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cutting Performance | Clean cut, minor filing needed | Smooth cut, no finishing required | Perfect flush cut, rounded edges |
| Tension Consistency | ±10% variation | ±5% variation | ±2% variation |
| Durability Rating | 10,000 cycles | 25,000 cycles | 50,000+ cycles |
| Warranty Coverage | 90 days | 1 year | 2+ years with repair service |
Troubleshooting Common Stainless Steel Zip Tie Tool Problems
Cutting Issues
Problem: Rough or incomplete cuts
- Cause: Dull cutting blade or improper blade alignment
- Solution: Replace cutting blade following manufacturer specifications
- Prevention: Regular blade inspection and replacement every 5,000 cuts
Problem: Tie tail not cut flush
- Cause: Worn blade guide or damaged cutting mechanism
- Solution: Professional service or blade guide replacement required
- Prevention: Avoid forcing oversized ties through tool
Tensioning Problems
Problem: Inconsistent tension application
- Cause: Worn tensioning spring or damaged ratchet mechanism
- Solution: Spring replacement or professional calibration service
- Prevention: Regular cleaning and lubrication per manufacturer schedule
Problem: Tool won’t reach preset tension
- Cause: Binding in feed mechanism or damaged tension adjustment
- Solution: Complete disassembly, cleaning, and recalibration
- Prevention: Use only specified tie sizes and avoid forcing damaged ties
Feed and Loading Issues
Problem: Tie won’t feed properly through slot
- Cause: Damaged or bent tie, debris in feed slot
- Solution: Clean feed slot thoroughly, inspect ties before loading
- Prevention: Store ties in protective containers, avoid dropping tools
Safety Requirements and Code Compliance
OSHA Safety Standards
Personal Protective Equipment Requirements
- Eye protection: Safety glasses or face shield mandatory during operation
- Hand protection: Cut-resistant gloves recommended when handling stainless steel ties
- Hearing protection: Required in production environments with pneumatic tools
Workplace Safety Protocols
- Tool inspection: Daily visual inspection for damage or wear
- Training requirements: Proper operator training on tool-specific procedures
- Maintenance scheduling: Regular preventive maintenance per manufacturer specifications
Electrical Code Compliance
NEC Article 320 Requirements
- Stainless steel ties must meet UL 62275 standards for electrical applications
- Minimum tensile strength requirements vary by application voltage
- Fire-rated installations require UL recognized cable tie materials
Installation Standards
- Maximum bundle diameter limits prevent conductor damage
- Proper spacing requirements maintain heat dissipation
- Grounding considerations for metal tie installations in electrical systems
Maintenance and Tool Care Best Practices
Daily Maintenance Checklist
- ✓ Visual inspection of cutting blade for chips or damage
- ✓ Feed slot cleaning to remove metal debris and contamination
- ✓ Handle operation check for smooth action and proper spring return
- ✓ Tension adjustment verification using calibrated test ties
Weekly Maintenance Tasks
- ✓ Detailed cleaning of all moving parts with compressed air
- ✓ Lubrication of pivot points with manufacturer-specified lubricant
- ✓ Cutting blade sharpness test using standard test materials
- ✓ Calibration check with tension gauge for accuracy verification
Monthly Professional Service
- ✓ Complete disassembly and inspection by qualified technician
- ✓ Replacement of wear components before failure occurs
- ✓ Precision calibration using certified test equipment
- ✓ Documentation update of service records and cycle counts
💡 Expert Tip: Keep detailed maintenance logs to predict component replacement needs and schedule preventive service before tool failure impacts productivity.
Frequently Asked Questions
What tension should I use for electrical applications?
For electrical cable bundling, use 15-25 pounds tension to secure cables without damaging conductor insulation. Higher tensions may compress cables and affect electrical performance.
Can I use standard zip tie tools with stainless steel ties?
No, standard plastic zip tie tools lack the strength and cutting capability required for stainless steel ties. Attempting to use inappropriate tools will damage both the tool and the ties.
How do I know when to replace the cutting blade?
Replace the cutting blade when cuts become rough, require multiple attempts, or leave sharp edges that require filing. Typical blade life is 5,000-8,000 cuts under normal conditions.
What’s the difference between 304 and 316 stainless steel ties?
316 stainless steel offers superior corrosion resistance in marine and chemical environments, while 304 stainless steel provides good general-purpose performance at lower cost. Match material to environmental requirements.
Can pneumatic tools be used in explosive atmospheres?
Standard pneumatic zip tie tools are not rated for explosive atmospheres. Use only tools with proper ATEX or Class I, Division 1 certifications in hazardous locations.
How do I achieve consistent tension across multiple installations?
Calibrate your tool regularly using a tension gauge, maintain consistent operator technique, and use preset tension settings rather than operator feel for critical applications.
What bundle diameter limits should I observe?
Maximum bundle diameter should not exceed 80% of the tie’s rated loop capacity to ensure proper locking engagement and prevent tie failure under load.
Are there alternatives to stainless steel for harsh environments?
Consider nylon 6/6 with UV stabilizers for outdoor applications or PEEK ties for extreme chemical resistance, but stainless steel remains the best choice for combined strength, temperature, and corrosion resistance.
Professional Installation Standards and Best Practices
Quality Assurance Guidelines
Installation Inspection Criteria
- All ties properly tensioned without over-compression
- Cut edges smooth and flush with no protruding tails
- Bundle organization maintains service accessibility
- Proper spacing prevents chafing and wear points
Documentation Requirements
- Record tie specifications and installation tensions
- Document bundle configurations for maintenance reference
- Maintain tool calibration certificates for quality systems
- Photo documentation for critical or warranty applications
Expert Installation Tips
💡 Bundle Preparation: Pre-organize cables using temporary ties to maintain proper spacing during permanent installation.
💡 Environmental Considerations: Allow for thermal expansion in outdoor installations by slightly loosening ties in extreme cold conditions.
💡 Service Access: Install ties with cut tails positioned away from service areas to prevent injury during maintenance.
💡 Load Distribution: Use multiple smaller ties rather than single large ties for heavy bundles to distribute stress evenly.
Conclusion
Mastering the proper use of stainless steel zip tie tools is essential for professional-quality installations in demanding environments. Whether you choose manual tools for portability and cost-effectiveness or pneumatic tools for high-volume production, following proper techniques ensures safe, reliable, and code-compliant installations.
The key to success lies in matching tool capabilities to application requirements, maintaining equipment properly, and following established safety protocols. With proper training and quality tools, stainless steel zip tie installations provide decades of reliable service in the most challenging environments.
For complex installations or when code compliance questions arise, consult with qualified electrical contractors or mechanical engineers to ensure your application meets all relevant standards and safety requirements.