Terminal Blocks vs Cold-Pressed Terminals: Complete Comparison Guide for Electrical Connections
Quick Answer: Terminal blocks are reusable screw-type connectors that allow multiple wire connections in panels and junction boxes, while cold-pressed terminals are permanent crimp connectors that attach directly to individual wire ends for secure, vibration-resistant connections. Terminal blocks excel in control panels and distribution systems, while cold-pressed terminals are ideal for automotive, marine, and high-vibration applications.
Understanding the difference between terminal blocks and cold-pressed terminals is crucial for selecting the right electrical connection method for your specific application, ensuring both safety and reliability in your electrical installations.
What Are Terminal Blocks and Cold-Pressed Terminals?
Terminal Block Definition

A terminal block is a modular, screw-type electrical connector that allows multiple wires to be connected together in organized rows. These reusable connectors feature individual chambers with screw terminals that clamp down on stripped wire ends, creating secure electrical connections without permanent modification to the wires themselves.
Cold-Pressed Terminal Definition
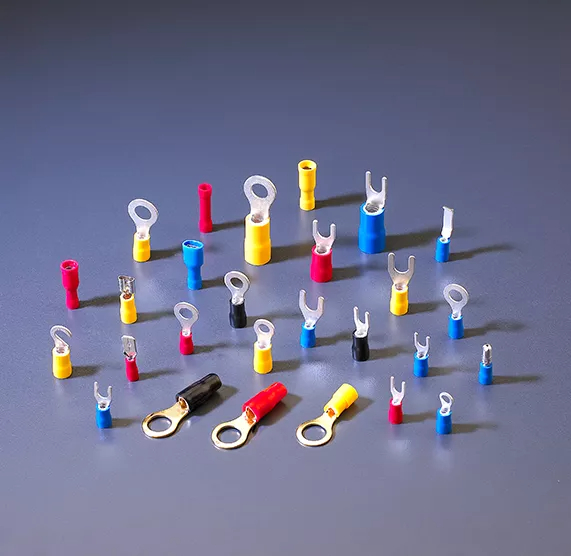

Cold-pressed terminals (also called crimp terminals or compression terminals) are permanent electrical connectors that attach to wire ends through mechanical compression using specialized crimping tools. The “cold-pressed” process creates a gas-tight connection without heat, forming a permanent bond between the terminal and wire conductor.
Key Differences Between Terminal Blocks and Cold-Pressed Terminals
| Feature | Terminal Blocks | Cold-Pressed Terminals |
|---|---|---|
| Connection Method | Screw-clamped, removable | Crimped, permanent |
| Reusability | Fully reusable | Single-use, permanent |
| Installation Speed | Moderate (requires stripping and screwing) | Fast (strip and crimp) |
| Vibration Resistance | Good with proper torque | Excellent, gas-tight seal |
| Current Capacity | 5A to 600A+ depending on size | 1A to 1000A+ depending on gauge |
| Typical Applications | Control panels, junction boxes | Automotive, marine, appliances |
| Cost per Connection | Higher initial, lower long-term | Lower per terminal |
| Space Requirements | Larger, requires mounting rail | Compact, wire-end only |
| Maintenance Access | Easy wire changes | Requires terminal replacement |
Applications and Use Cases
Terminal Block Applications
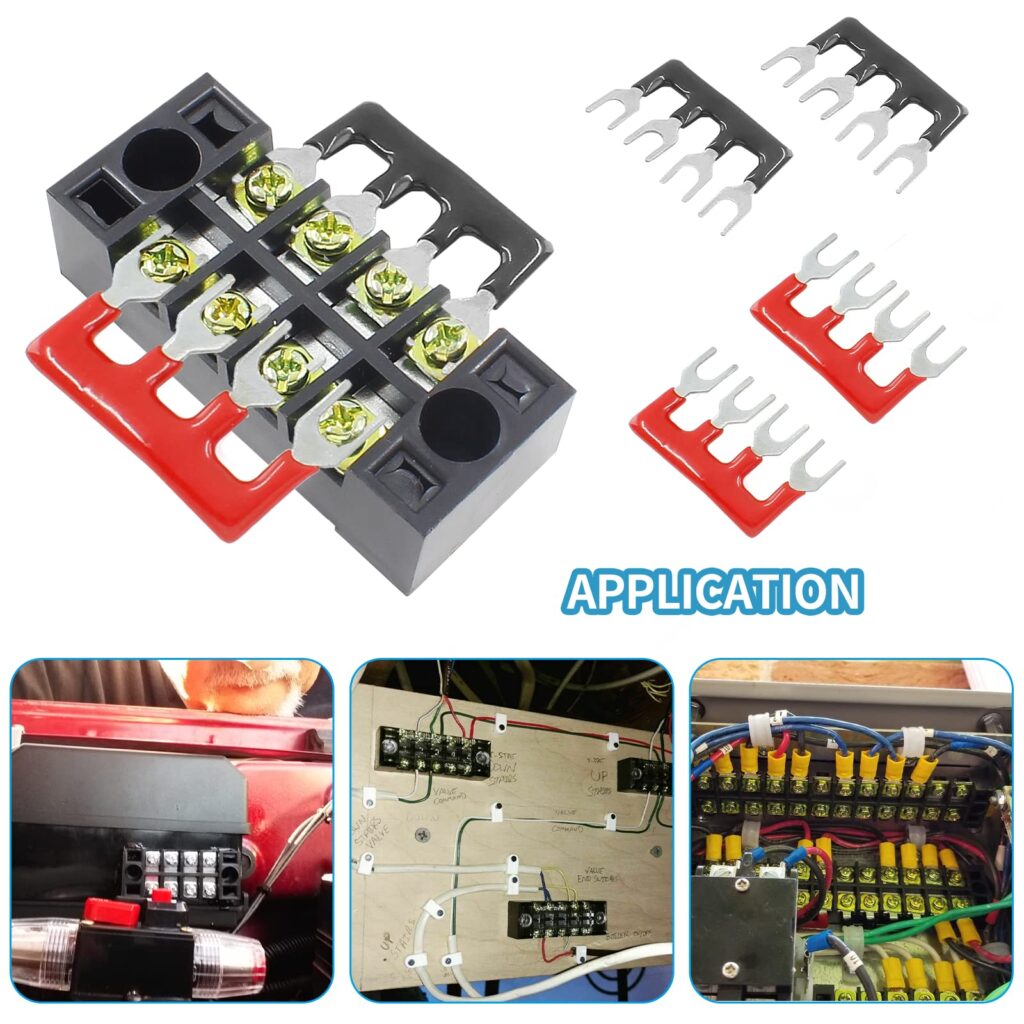

Control Panels and Distribution Systems
- Industrial control cabinets and PLCs
- Electrical distribution panels
- HVAC control systems
- Building automation systems
Advantages for Panel Work:
- Multiple wire connections per block
- Easy wire identification and labeling
- Quick troubleshooting and modifications
- Standard DIN rail mounting
Cold-Pressed Terminal Applications

High-Vibration and Mobile Environments
- Automotive electrical systems
- Marine and boat wiring
- RV and trailer connections
- Appliance internal wiring
Benefits for Mobile Applications:
- Superior vibration resistance
- Moisture and corrosion resistance
- Compact connection profile
- Permanent, reliable bond
Expert Tip: Choose terminal blocks for stationary equipment requiring frequent wire changes, and cold-pressed terminals for permanent connections in vibrating or harsh environments.
Selection Criteria: How to Choose the Right Connection
Choose Terminal Blocks When:
- Frequent modifications needed: Equipment requiring regular wire changes
- Multiple wire junctions: Several wires connecting at single points
- Panel organization: Clean, labeled wire management is priority
- Code compliance: NEC or IEC standards require removable connections
- Troubleshooting access: Easy wire removal for testing needed
Choose Cold-Pressed Terminals When:
- Permanent connections: Long-term installations without planned changes
- Vibration exposure: Mobile equipment or high-vibration environments
- Space constraints: Compact connections required
- Environmental challenges: Moisture, corrosion, or temperature extremes
- High reliability: Critical connections requiring maximum security
Professional Installation Guidelines
Terminal Block Installation Process
- Mount blocks on standard DIN rail per NEC 110.14 requirements
- Strip wires to manufacturer’s specified length (typically 10-12mm)
- Insert wires fully into terminal chambers
- Torque screws to specified values (typically 4-8 in-lbs)
- Label connections according to electrical drawings
- Test connections with gentle pull test
Safety Warning: Always de-energize circuits before making connections. Use proper torque specifications to prevent loose connections that can cause arcing and fires.
Cold-Pressed Terminal Installation Process
- Select correct terminal size for wire gauge and application
- Strip wire to terminal manufacturer’s specifications
- Insert wire fully into terminal barrel
- Crimp using calibrated tool with proper die set
- Pull test connection at 20 pounds minimum force
- Inspect crimp for proper compression and wire contact
Expert Tip: Use ratcheting crimp tools with calibrated dies for consistent, reliable cold-pressed connections. Poor crimps are a leading cause of electrical failures.
Safety and Code Compliance
NEC and Safety Requirements
Both connection types must comply with National Electrical Code (NEC) requirements:
NEC 110.14 Electrical Connections:
- Proper torque specifications for terminal blocks
- Appropriate wire gauge ratings
- Temperature and environmental ratings
UL Listing Requirements:
- Terminal blocks: UL 1059 standard
- Cold-pressed terminals: UL 486 standard
Common Safety Issues
Terminal Block Hazards:
- Under-torqued connections causing overheating
- Over-torqued connections damaging wire strands
- Improper wire strip length causing poor contact
Cold-Pressed Terminal Hazards:
- Under-crimped connections creating high resistance
- Over-crimped connections damaging conductors
- Wrong terminal size for wire gauge
Cost Analysis and Long-Term Value
Initial Cost Comparison
| Connection Type | Material Cost | Tool Cost | Labor Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Terminal Blocks | $2-50 per block | $50-200 (screwdrivers, torque tools) | 2-3 minutes per connection |
| Cold-Pressed | $0.10-5 per terminal | $100-500 (crimp tools) | 30-60 seconds per connection |
Long-Term Value Considerations
Terminal Blocks:
- Higher upfront cost, lower maintenance cost
- Easy wire replacement without new components
- Reduced inventory requirements
Cold-Pressed Terminals:
- Lower per-connection cost
- Higher reliability in harsh environments
- Reduced maintenance labor in permanent installations
Troubleshooting Common Problems
Terminal Block Issues
Problem: Loose connections and overheating
Solution: Check torque specifications and retighten to manufacturer requirements
Problem: Wire strands damaged during installation
Solution: Use proper wire stripping technique and avoid over-torquing
Cold-Pressed Terminal Issues
Problem: Poor crimp connection with high resistance
Solution: Use calibrated crimping tools with proper die sets for wire gauge
Problem: Terminal pullout from wire
Solution: Verify correct terminal size and ensure full wire insertion before crimping
Quick Reference Guide
Wire Gauge Compatibility Chart
| Wire Gauge (AWG) | Terminal Block Range | Cold-Pressed Terminal Types |
|---|---|---|
| 22-14 AWG | 2.5mm² blocks | Ring, spade, butt connectors |
| 12-10 AWG | 4mm² blocks | Heavy-duty rings and spades |
| 8-6 AWG | 6-10mm² blocks | Large ring and lug terminals |
| 4 AWG and larger | 16mm²+ blocks | Compression lugs and rings |
Tool Requirements Checklist
Terminal Blocks:
- ✓ Calibrated torque screwdriver (2-10 in-lbs range)
- ✓ Wire strippers (10-12mm strip length)
- ✓ Multimeter for continuity testing
- ✓ Labels and markers for identification
Cold-Pressed Terminals:
- ✓ Ratcheting crimp tool with appropriate dies
- ✓ Wire strippers matched to terminal requirements
- ✓ Pull-test gauge (20+ pound capacity)
- ✓ Heat shrink tubing for environmental protection
Frequently Asked Questions
What makes terminal blocks better than wire nuts for panel work?
Terminal blocks provide organized, labeled connections with consistent torque specifications and better access for troubleshooting compared to wire nuts, which are primarily designed for junction box applications.
Can cold-pressed terminals be reused if I need to change wires?
No, cold-pressed terminals create permanent connections. Attempting to remove and reuse them compromises the connection integrity and violates electrical codes.
Which connection type handles higher current ratings?
Both can handle high currents when properly sized. Large terminal blocks can handle 600A+, while compression lugs (cold-pressed) can handle 1000A+ in utility applications.
Are cold-pressed terminals suitable for outdoor applications?
Yes, when properly selected with appropriate environmental ratings and used with heat shrink or other environmental protection, cold-pressed terminals excel in outdoor and marine applications.
How often should terminal block connections be inspected?
NEC recommends annual inspection of accessible electrical connections, with torque verification every 3-5 years depending on environmental conditions and criticality.
What’s the most common mistake when installing these connection types?
For terminal blocks: improper torque (usually under-torquing). For cold-pressed terminals: using the wrong size terminal for the wire gauge or inadequate crimping pressure.
Professional Recommendations
For optimal electrical system performance, consult with licensed electricians for applications involving:
- High-current connections (over 100 amps)
- Critical system installations
- Code compliance verification
- Complex multi-wire junction requirements
Both terminal blocks and cold-pressed terminals serve essential roles in electrical systems. Choose based on your specific application requirements, environmental conditions, and long-term maintenance needs to ensure safe, reliable electrical connections that meet code requirements and provide years of trouble-free operation.