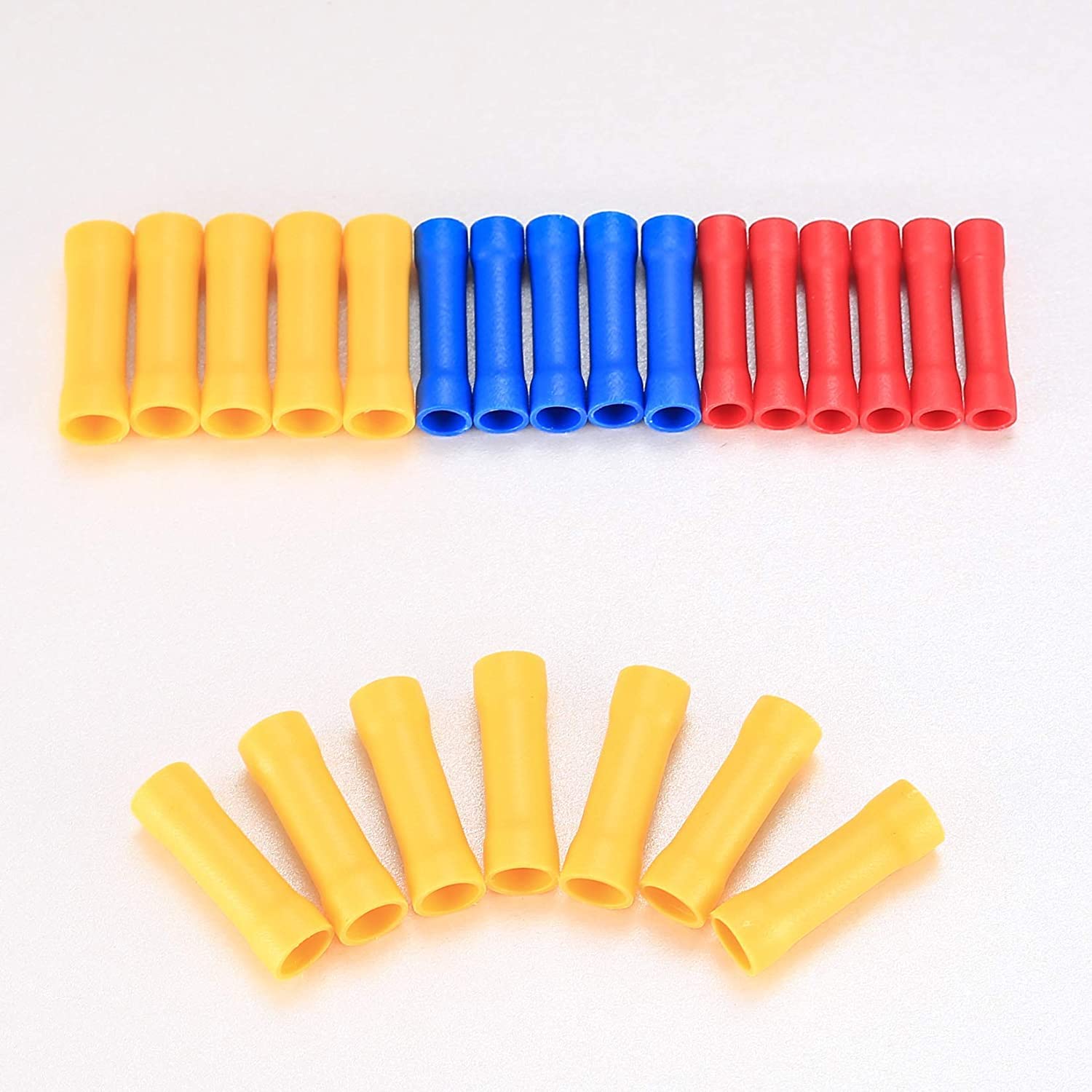
Quick Answer: Butt splice connectors are electrical joining devices that connect two wire ends end-to-end, creating a continuous electrical path. They’re primarily used in automotive wiring, home electrical repairs, and industrial applications where secure, permanent wire connections are needed.
Understanding butt splice connector applications is crucial for anyone working with electrical systems, from DIY enthusiasts to professional electricians. These versatile connectors provide reliable, code-compliant connections that ensure electrical safety and system performance.
What Are Butt Splice Connectors?
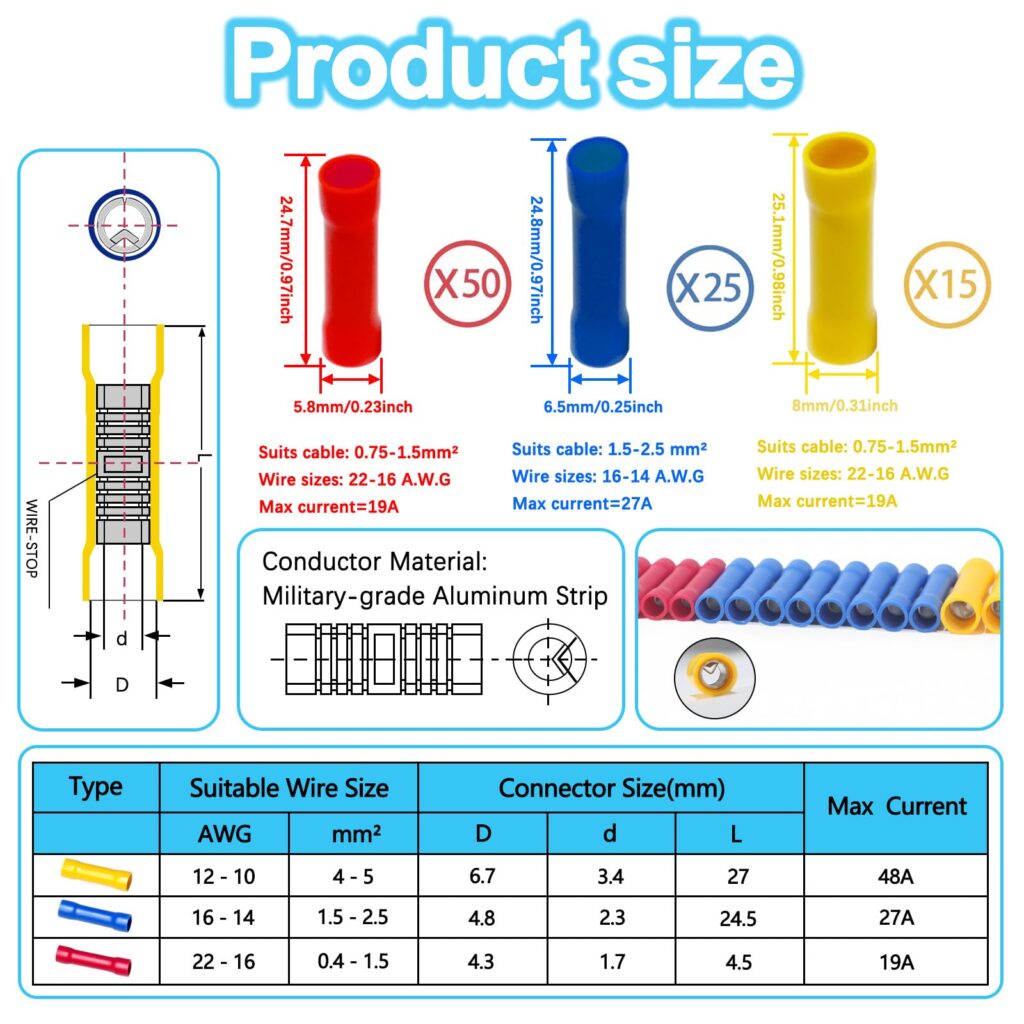
A butt splice connector is a cylindrical electrical connector designed to join two wire ends by inserting each wire into opposite ends of the connector. The connection is typically secured through crimping, soldering, or heat-shrink technology, creating a permanent electrical joint.
Key Characteristics:
- Cylindrical design for end-to-end wire joining
- Available in various sizes for different wire gauges
- Made from conductive materials like copper or aluminum
- Often includes insulation for safety and protection
Butt Splice vs. Other Wire Connectors: Complete Comparison
Here is a table that shows the key differences between butt splice connectors and other common electrical connectors:
| Connector Type | Connection Method | Permanence | Best Applications | Wire Gauge Range | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Butt Splice | End-to-end crimping | Permanent | Wire extensions, repairs | 10-22 AWG | Low |
| Wire Nuts | Twisting/threading | Semi-permanent | Junction boxes, home wiring | 12-22 AWG | Very Low |
| Terminal Blocks | Screw/spring clamp | Removable | Control panels, distribution | 6-24 AWG | Medium |
| Lever Nuts | Spring mechanism | Removable | Quick connections, panels | 12-24 AWG | Medium |
| Solder Joints | Molten metal fusion | Permanent | Circuit boards, precision work | All sizes | Low |
Primary Applications of Butt Splice Connectors

1. Automotive Electrical Systems
Why They’re Essential:
- Vibration resistance in moving vehicles
- Moisture protection in harsh environments
- Space-efficient design for cramped areas
- Temperature stability for engine compartments
Common Automotive Uses:
- Headlight and taillight wiring repairs
- Speaker wire connections in audio systems
- Engine sensor wire extensions
- Trailer wiring harness connections
2. Home Electrical Repairs
Residential Applications:
- Extending short wires during renovations
- Repairing damaged cable runs
- Connecting new fixtures to existing wiring
- Underground sprinkler system wiring
⚠️ Safety Note: Always follow NEC (National Electrical Code) requirements for residential wiring. Many home applications require junction boxes rather than inline splices.
3. Industrial and Commercial Wiring
Industrial Uses:
- Control panel interconnections
- Motor and equipment wiring
- Lighting system repairs in warehouses
- Conveyor system electrical connections
Benefits in Industrial Settings:
- High current-carrying capacity
- Chemical resistance
- Temperature tolerance
- Compliance with industrial codes
Types of Butt Splice Connectors
Standard Crimp Connectors
Features:
- Copper or tin-plated construction
- Requires crimping tool for installation
- Available in insulated and non-insulated versions
- Most economical option
Best For: General-purpose electrical connections in dry environments
Heat Shrink Butt Splices
Advanced Features:
- Built-in heat-shrink tubing
- Waterproof seal when properly installed
- Color-coded for different wire gauges
- Enhanced corrosion protection
Best For: Outdoor applications, marine wiring, automotive repairs
Solder Sleeve Connectors
Professional-Grade Features:
- Pre-loaded with flux-core solder
- Heat-activated connection process
- Superior electrical conductivity
- Excellent for high-vibration environments
Best For: Aerospace, military, and high-reliability applications
How to Select the Right Butt Splice Connector
Wire Gauge Compatibility
Here is a table that shows proper connector sizing for different wire gauges:
| Wire Gauge (AWG) | Connector Size | Crimp Tool Die | Maximum Current | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 22-18 | Red | Small | 15A | Control circuits, sensors |
| 16-14 | Blue | Medium | 20A | Lighting, small motors |
| 12-10 | Yellow | Large | 30A | Branch circuits, larger motors |
| 8-6 | Uninsulated | Extra Large | 50A+ | Service panels, heavy equipment |
Environmental Considerations
Choose Based on Conditions:
- Dry indoor locations: Standard crimp connectors
- Outdoor/wet areas: Heat shrink or waterproof versions
- High-vibration areas: Solder sleeve or professional-grade crimps
- Corrosive environments: Tin-plated or stainless steel options
Step-by-Step Installation Process
For Standard Crimp Connectors:
- Strip wire insulation 3/8 inch from each wire end
- Select proper connector size based on wire gauge
- Insert first wire fully into one end of connector
- Crimp connection using appropriate die size
- Insert second wire into opposite end
- Crimp second connection ensuring full compression
- Test connection with gentle pull test
- Apply electrical tape if additional insulation needed
For Heat Shrink Connectors:
- Strip wires to proper length (typically 1/4 inch)
- Insert wires into connector ends until they meet in center
- Apply heat evenly around connector using heat gun
- Watch for shrink activation and solder flow (if applicable)
- Allow cooling before handling
- Verify seal integrity and electrical continuity
🔧 Expert Tip: Always use a proper crimping tool with calibrated dies. Pliers or other makeshift tools can create unreliable connections that may fail under load.
Safety Requirements and Code Compliance
National Electrical Code (NEC) Guidelines
Key NEC Requirements:
- Splices must be accessible for inspection
- All connections require proper enclosures in most applications
- Wire nuts preferred over splices in residential junction boxes
- Underground installations need waterproof methods
OSHA Workplace Safety Standards
Compliance Requirements:
- De-energize circuits before making connections
- Use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE)
- Follow lockout/tagout procedures
- Ensure proper grounding of equipment
Common Problems and Troubleshooting
Connection Failures
Symptoms:
- Intermittent electrical operation
- Excessive heat at connection point
- Voltage drop across splice
- Complete circuit failure
Solutions:
- Verify proper crimp compression
- Check for corrosion or oxidation
- Ensure adequate wire strip length
- Replace with appropriate connector size
Environmental Damage
Prevention Strategies:
- Use heat shrink connectors in wet locations
- Apply dielectric grease in corrosive environments
- Protect connections from physical damage
- Follow temperature rating specifications
⚠️ Safety Warning: Never attempt electrical work on live circuits. Always turn off power at the breaker and verify with a multimeter before beginning work.
When to Call a Professional
Professional Help Required:
- Main service panel connections
- High-voltage applications (over 240V)
- Code compliance questions
- Complex commercial installations
DIY-Appropriate Projects:
- Low-voltage landscape lighting
- Automotive electrical repairs
- Speaker wire connections
- 12V DC system repairs
Selection Criteria Checklist
Before Choosing Butt Splice Connectors, Consider:
- ✓ Wire gauge compatibility
- ✓ Environmental conditions (wet/dry, temperature)
- ✓ Current carrying requirements
- ✓ Code compliance needs
- ✓ Installation tool availability
- ✓ Long-term reliability requirements
- ✓ Cost vs. performance needs
Expert Tips for Professional Results
🔧 Pro Installation Tips:
- Proper Strip Length: Too little creates weak connections; too much exposes unnecessary wire
- Crimp Quality: A proper crimp should show slight barrel deformation
- Tool Calibration: Check crimping tools annually for consistent results
- Environmental Protection: When in doubt, use heat shrink versions
- Testing: Always perform continuity and pull tests before energizing
Frequently Asked Questions
What’s the difference between butt splice connectors and wire nuts?
Butt splice connectors join wires end-to-end and create permanent connections, while wire nuts twist multiple wires together and can be removed. Butt splices are better for extending wire runs, while wire nuts are preferred for junction box connections.
Can butt splice connectors be used in household electrical panels?
No, butt splice connectors should not be used inside electrical panels. Panel connections require specific torque specifications and are typically made with wire nuts or terminal blocks designed for panel use.
How do I know if my crimp connection is secure?
A proper crimp connection should show slight deformation of the connector barrel, hold the wire securely under gentle pull testing, and maintain electrical continuity. The wire should not pull out with moderate force.
Are heat shrink butt splices waterproof?
When properly installed with adequate heat application, heat shrink butt splices provide excellent moisture resistance. However, they should not be considered completely waterproof for permanent submersion applications.
What wire gauge range do butt splice connectors handle?
Standard butt splice connectors typically handle wire gauges from 22 AWG to 10 AWG, with specialized versions available for larger conductors up to 6 AWG or smaller wire down to 24 AWG.
Can aluminum wire be used with butt splice connectors?
Some butt splice connectors are rated for aluminum wire, but you must verify compatibility. Look for connectors marked “AL” or “CU/AL” and ensure proper anti-oxidation compounds are used.
How long do butt splice connections last?
When properly installed with appropriate connectors for the environment, butt splice connections can last 20+ years in residential applications and 10+ years in harsh automotive environments.
Do butt splice connectors affect voltage drop?
Properly installed butt splice connectors add minimal resistance and should not cause noticeable voltage drop. Poor connections, however, can create significant voltage loss and heat buildup.
Conclusion
Butt splice connectors provide reliable, permanent electrical connections for automotive, residential, and industrial applications when properly selected and installed. Choose the right type based on your environment, wire gauge, and code requirements. Always prioritize safety by following proper installation procedures and seeking professional help for complex electrical work.
For permanent, code-compliant electrical connections, butt splice connectors offer an efficient solution that balances cost, reliability, and installation simplicity. Remember to always verify local electrical codes and consider professional consultation for critical applications.
Need professional electrical work? Consult with a licensed electrician to ensure code compliance and safety in your electrical projects.